|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
| 丂Introduction
丂Ultrafine-grain strengthening is effective to increase strength without alloying elements. Dual phase strengthening also plays an important role to improve a balance between strength and elongation.
丂丂In this study, tensile tests with strain rates between 10-6 and 10-2 s-1 at low temperatures below room temperature are performed for ferrite-pearlite (FP) steels with ferrite grain sizes of 3.6, 9.8 and 46.2 mm. I investigate effects of temperature, strain rate and ferrite grain size on flow stress for the FP steels based on the experimental results.
丂
|
|
 |
|
 |
|
| 丂Experimental Procedure
丂Three FP steels with ferrite grain sizes of 3.6, 9.8 and 46.2 mm were prepared by microstructural control with a JIS-SM490 (0.15C-0.4Si-1.5Mn-0.014P-0.004S(mass%))steel.
|
|
|
|
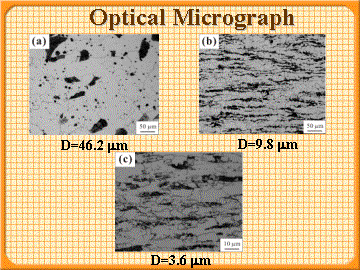 |
|
|
| Tensile tests with strain rates of 10-6, 10-4 and 10-2 s-1 were conducted at 77 K (in liquid nitrogen), 210 K (in methanol) and 296 K (in air) by using a gear-driven type Instron machine. |
|
|
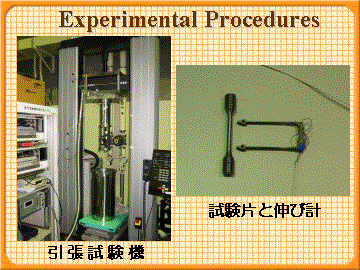 |
|
|
 |
|
|
|
| 丂Results and discussions
1. Stress-strain curves and tensile properties
|
|
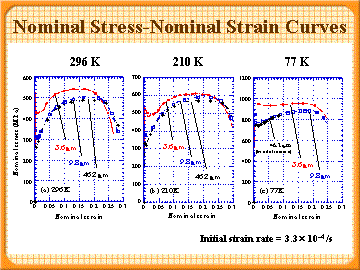 |
Nominal stress-nominal strain curves
(Initila strain rate=3.3亊10-4 /s)
|
|
- Flow stress increases with decreasing of ferrite grain size and temperature.
- The FP steel with 46.2 mm shows brittle fracture at 77 K.
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
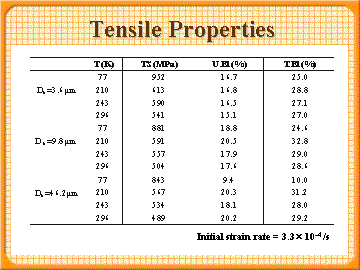
Tensile properties (Tensile strength (TS), Uniform elongation (U.El),Total elongation (T.El))
|
|
- U.El and T.El at each temperature decreases with decreasing of ferrite grain size.
|
|
|
2. Effect of ferrite grain size on flow stress |
|
|
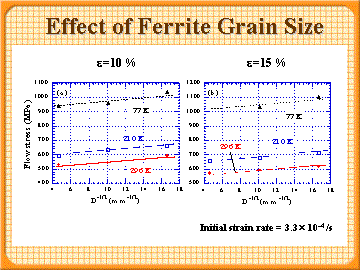 |
10% and 15% flow stresses as afunction of inverse square root of ferrite grain size
|
|
- Both of 10% flow stress, 15% flow stress can be described by the Hall-Petch relation.
- The slope k of the Hall-Petch equation is almost independent of temperature and strain rae.
|
|
|
3. Effects of temperature and strain rate on flow stress |
|
|
 |
|
|
|
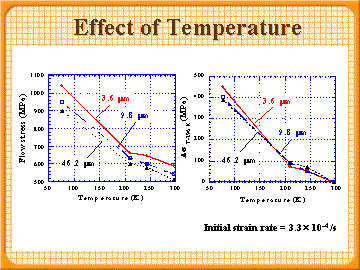
10% flow stress as according to temperature
- The change of flow stress with temperature is almost independent of ferrite grain size.
|
|
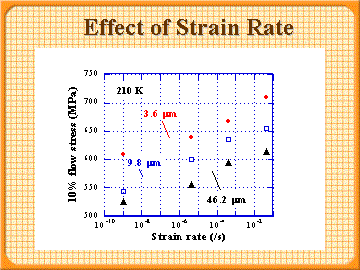 |
10% flow stress according to strain rate
- The change of flow stress with strain rate is also almost independent of ferrite grain size.
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 丂Summary |
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
丂Next
- High-speed deformation of the ultrafine-grained FP steel
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
E-mail: (tsuchida@eng.u-hyogo.ac.jp) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|